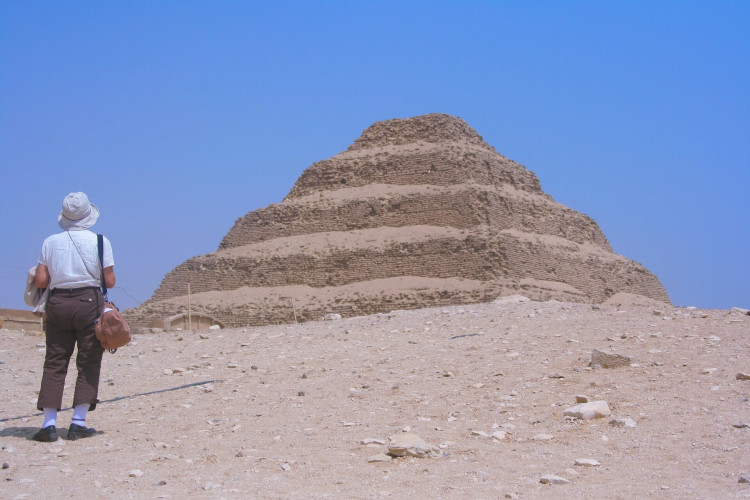
Stepped Pyramid at Saqqara (Egypt) - called the pyramid of Djoser of the eighteenth century BC
Where is located Step Pyramid?
Address of Step Pyramid is Saqqara, Egypt
show on map
When was built Step Pyramid?
Built date of Step Pyramid is XXVII in. P.n.e.

Facts, informations and history of Step Pyramid
Sakkara's necropolis took its name from a small village and was part of the memphis necropolis.
The step pyramid, also known as the Djoser pyramid, was built by the first architect in world history - Imhotep, who was also the discoverer of the method of building of hewn stones.
The pyramid was built on a rectangular plan with a long terrace from the forehead. It has a surface area of 121 x 109 and is 58.8 m high. It was created on the basis of square mastaba (the tomb of pharaohs and dignitaries, the aboveground part - cuboid with sloping walls with blind gates and serdab (room with a statue of the deceased), underground part - shaft and burial chamber).
In the center of the pyramid there is the burial chamber of Djoser. When the king's mummy was put in it, it was closed with a granite block weighing three tons. There are also eleven other shafts for the burial site of queens and prematurely deceased royal children.
"The more time we devote to observing this place, the greater admiration we get." - Adellatif
Architect of Step Pyramid

How many meters have Step Pyramid?
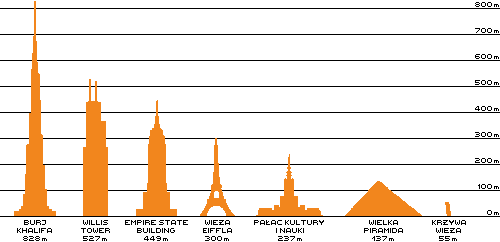
Height of Step Pyramid is 58.8 m

Construction/building type
Building Step Pyramid is of type Pyramid
The pyramid is one of the most recognisable architectural forms that has a long history and is found in various cultures around the world. Here is some information about the pyramids, its precursors and the most famous structures of this type.... czytaj więcej.
Other dimensions, parameters and frequently asked questions

What area have Step Pyramid?
Step Pyramid have area of 13189 m²
What material is the building made of?
Step Pyramid is made of the following materials: Stone
Other names
The building is also known by other common names or in the original language, i.e. Piramida Dżesera
Is the building on the UNESCO World Heritage List?

The listing took place in the year 1979.
Details of the entry are available on the Unesco website at https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/86/
Photo gallery Add photo
Location on map / How to get there















Comments to Step Pyramid (18) Average rating: 4,0 Add comment / Rate building
Based on 18 comments